나이아신아마이드(Niacinamide)
페이지 정보
작성자 최고관리자 작성일 24-01-22 08:06 조회 5,222 댓글 0본문
1. 성분명
나이아신아마이드
니코틴아마이드
niacinamide
nicotinamide
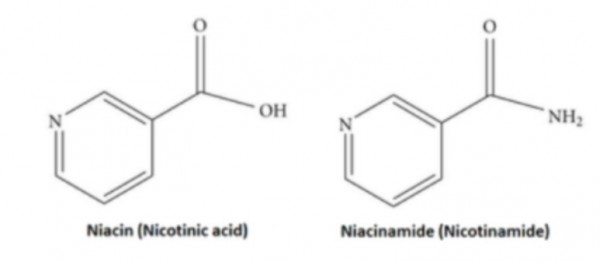
2. 구조식
나이아신에 암모니아(NH3)가
아미드 결합된 물질
(나이아신 = 비타민 B3)
※ 아미드 결합
- COOH 와 -NH3가 결합하는 탈수축합반응
펩타이드결합도 아미드결합에 속함.
3. SKIN DEEP(EWG)
1
4. 원료 제조사
DSM (스위스)
PLAMED(중국)
Anne Wang N&R Bio Industries Inc. (중국)
MakingCosmetics(미국)
5. 화장품 용도
6. 화장품 효능
DOS PAW 모두 효능
1. 미백
화장품에 2~5% 포함시
식약청 고시 미백기능성 성분
멜라닌세포에서 각질세포로
멜라노좀의 이동을 억제
2. 항염
여드름, 홍조와 같은
염증성 피부 질환에 도움을 줍니다.
Within a complex metabolic system
niacinamide controls the NFκB-mediated transcription of signalling molecules
by inhibiting the nuclear poly ADP-ribose polymerase-1 (PARP-1).
3. 피지감소
5a reductase type 1억제
4. 보습
세라마이드 합성에 필요한
serine-palmitoyl transperase를 증가시켜
세라마이드 합성을 촉진 시킨다.
5. 주름개선
진피의 콜라겐합성 증가로 주름 개선
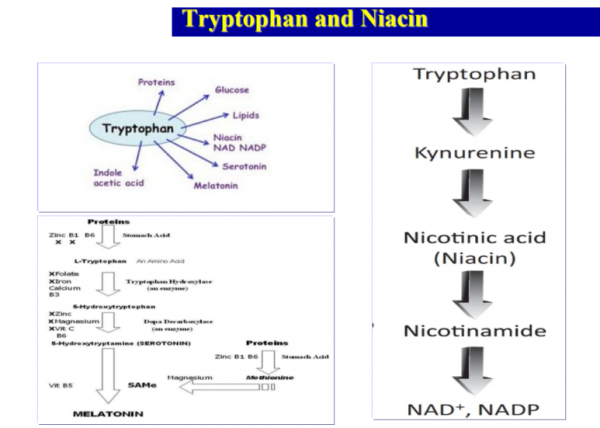
7. 역사
니코틴산은 니코틴의 산화로 발생되는 부산물로
1867 년에 최초로 합성되어
사진인화에 널리 사용되었습니다.
독일 과학자들이 니코틴산이 효모와 쌀에서
발생한다는 사실을 입증하기 전까지는
음식/건강/피부와 관련이 없다고 오랫동안 생각되었습니다.
8. 복용시 효능
펠라그라: 나이아신 부족에의한 질환
3D: dermatitis, dementia, diarrhea
펠라그라의 치료제
9. 기타
NMN
https://m.blog.naver.com/dr_oracle_/222363293117
NAD
https://m.blog.naver.com/dr_oracle_/222358236071
● 성상
1) 분자량
122.13 g/mol
2) 실온형상
흰색 고체 파우더
3) 끓는점
334.4 ℃
4) 녹는점
156 ℃
● Kg당 가격
1kg 당 대략 8,000~15,000원
● 10% 농도 사용시 피부자극 유발 가능
나이아신아마이드 10% 함량은 기능성 보고가 아닌 기능성 심사로 해야하며, 독성시험, 자극시험, 피부 감작성 시험, 광독성 및 광감작성 시험, 첩포시험, 효력시험, 인체적용시험 등 자료를 제출해야 한다.
(참조)
※ 참고
Given a sufficient bioavailability, niacinamide has antipruritic, antimicrobial, vasoactive, photo-protective, sebostatic and lightening effects depending on its concentration. Within a complex metabolic system niacinamide controls the NFκB-mediated transcription of signalling molecules by inhibiting the nuclear poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1).
※ 인용논문
1. Bender 2003. Nutritional Biochemistry of the Vitamins. Cambridge University Press. p. 203. ISBN 978-1-139-43773-8. Archived from the original on 2016-12-30.
2. Berge et al. 2006. Niacinamide-Containing Facial Moisturizer Improves Skin Barrier and Benefits Subjects with Rosacea. Therapeutics for the Clinician. Retrieved from (https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/c866/417320abb8a6d79791d10ad66c6acc6b22d2.pdf)
3. Bissett, D. L., Oblong, J. E., & Berge, C. A. (2005). Niacinamide: AB vitamin that improves aging facial skin appearance. Dermatologic surgery, 31, 860-866.
4. British National Formulary: BNF 69 (69th ed.). British Medical Association. 2015. p. 822. ISBN 978-0-85711-156-2.
5. Decker et al. 2012. Over-the-counter acne treatments: a review. The Journal of clinical and aesthetic dermatology, 5(5), 32. Retreived from (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3366450/pdf/jcad_5_5_32.pdf)
6. Esfahani, Soheil Ashkani, et al. "Topical nicotinamide improves tissue regeneration in excisional full-thickness skin wounds: A stereological and pathological study." Trauma monthly 20.4 (2015).
7. Gehring 2004. Nicotinic acid/niacinamide and the skin. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology. Retrieved from (https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1473-2130.2004.00115.x)"
8. Hakozaki et al. 2002. The effect of niacinamide on reducing cutaneous pigmentation and suppression of melanosome transfer. British Journal of Dermatology. Retrieved from (https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1046/j.1365-2133.2002.04834.x)
9. Jacobson, et al. 2007. A topical lipophilic niacin derivative increases NAD, epidermal differentiation and barrier function in photodamaged skin. Experimental dermatology, 16(6), 490-499.
10. Kenneth S. et al. 2006. The effect of 2% niacinamide on facial sebum production. Journal of Cosmetic and Laser Therapy. Retrieved from (https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/14764170600717704)
11. Kimball et al. 2010. Reduction in the appearance of facial hyperpigmentation after use of moisturizers with a combination of topical niacinamide and N‐acetyl glucosamine: results of a randomized, double‐blind, vehicle‐controlled trial. British Journal of Dermatology. Retrieved from (https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1365-2133.2009.09477.x)
12. Who Model Formulary 2008. World Health Organization. 2009. pp 496, 500. ISBN 978-924-154765-9. Archived from the original on December 13, 2016. Retrieved December 8, 2016.
13. Wohlrab et al. 2014. Niacinamide-mechanisms of action and its topical use in dermatology. Skin pharmacology and physiology, 27(6), 311-315.
#나이아신아마이드
#니코틴아마이드
#niacinamide
#nicotinamide
댓글목록 0
등록된 댓글이 없습니다.