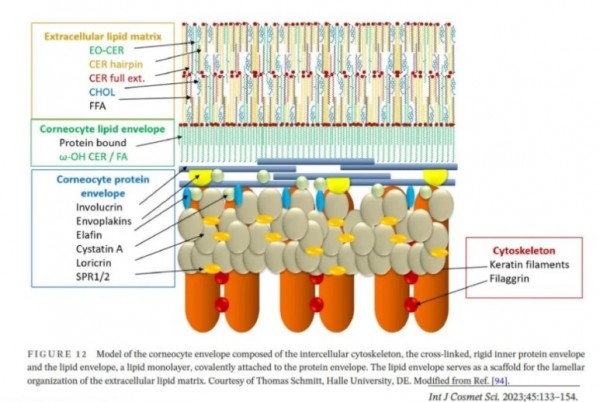
세라마이드(Ceramide)
페이지 정보
작성자 최고관리자 작성일 24-01-22 05:43 조회 5,264 댓글 0본문
1.성분명
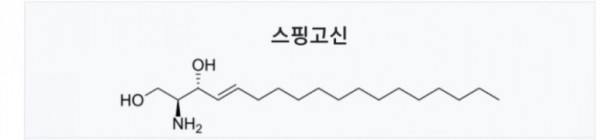
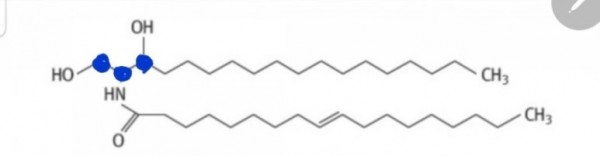
세라마이드(Ceramide)
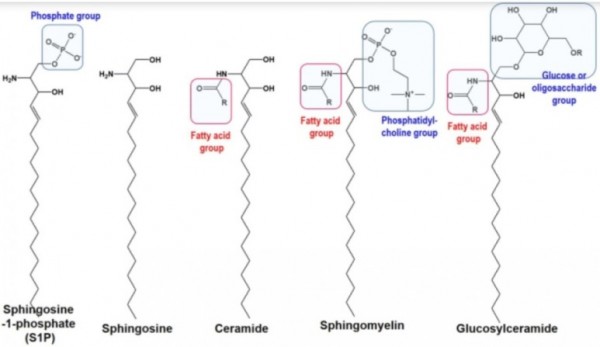
※ 세라마이드는
스핑고이드 베이스에
지방산이 결합된 분자
■ 세라마이드 = 스핑고이드 + 지방산
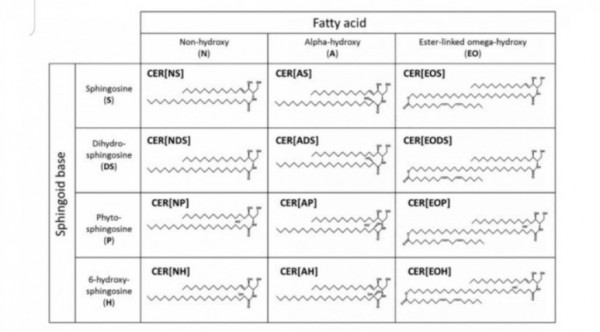
※ 스핑고이드 베이스 4종
P : 파이토스핑고신
S : 스핑고신
H : 6-하이드록시스핑고신
DS : 다이하이드록시스핑고신
※지방산 5종
N : neutral
A : alpha-hydroxy
EO : ester linked omega hydroxy
O : Omega hydroxy
EN : 1-O-acylceramide
==>
4×5 =20종의 세라마이드 존재 예측
NP NS NH NDS
AP AS AH ADS
EOP EOS EOH EODS
OP OS OH ODS
ENP ENS ENH ENDS
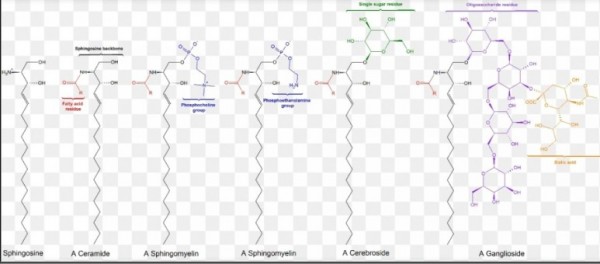
세라마이드 전구체인 스핑고이드(Sphingoids)와 결합되는 지방산의 구조에 의해
다양한 세라마이드가 존재한다.
피부에 존재하는 세라마이드는
이론적으로 20개가 존재하나,
현재까지는 15종이 발견되었다.
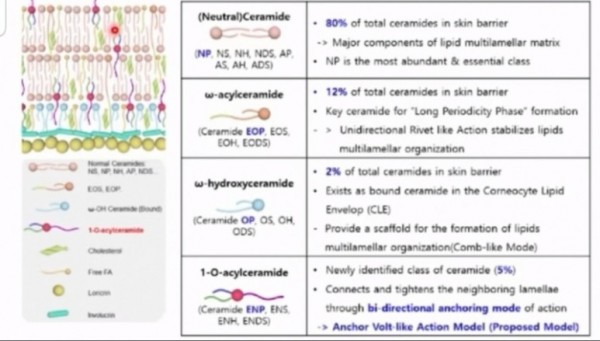
세라마이드는 크게 4가지
NP(NP,AP), EOP, OP, ENP로
구분되어지며,
각기 중요한 역할을 담당하고 있는데,
최근에는 새롭게 발견된
1-O-acylceramide에 대한 연구가
활발하게 진행되고 있다.
1-O-acylceramide는 ENP에 속하는 것으로 각질세포에서 라멜라를
양방향에서 고정시킴으로써
라멜라 구조를 안정화시키는
역할을 한다.
※ Ceramides are a family of waxy lipid molecules.
A ceramide is composed of sphingosine and a fatty acid.
Ceramides are found in high concentrations
within the cell membrane
of eukaryotic cells,
since they are component lipids
that make up sphingomyelin,
one of the major lipids in the lipid bilayer.[1]
Contrary to previous assumptions that ceramides and other sphingolipids found
in cell membrane were purely supporting structural elements, ceramide can participate in a variety of cellular signaling:
examples include regulating differentiation,
proliferation,
and programmed cell death (PCD) of cells.
※ 스핑고리피는 항암제로도 사용됨
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40005-020-00475-y
3. SKIN DEEP(EWG)
1등급
4. 원료 제조사
Evonik(독일)
Doosan(한국)
Grant Industries(미국)
※ 세라마이드는 약 20년 전에 개발되었는데
최근에 다시 재조명을 받고 있다.
Persistence Market Research의
시장보고서에 의하면,
글로벌 세라마이드 마켓은
향후 연평균 6.6% 성장률로
2029년에는 691.1M 달러
(한화 약 8,500억원)의
시장규모가 예상된다.
효모 유래 세라마이드
(Fermentation Ceramides)
시장이 60%이상을 차지할 것으로 보이며,
특히 중국시장은 연평균 8.8%로
글로벌 시장에 비해 높은
고성장을 할 것으로 전망된다.
5. 화장품 용도
피부컨디셔닝제
헤어컨디셔닝제
보습제 밀폐제
6. 효능
보습제
※ 스핑고신은
스핑고신 키네이스 1 및
스핑고신 키네이스 2에 의해
생체 내에서 인산화될 수 있다.
스핑고신의 인산화로 인해
강력한 신호 전달 지질인
스핑고신 1-인산(S1P)이 생성된다.
세라마이드, 스핑고신,
스핑고신 1-인산과 같은
스핑고지질의 대사산물들은
다양한 세포 신호전달 과정에 관여하는
지질 신호전달 분자이다.
※ 지방산과 콜레스테롤 인지질도
지질 신호전달 물질임.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nuclear_receptor#Ligands
7. 역사
※ 피부장벽 구조는 1990년 초중반에
피터 일라이스(Peter Elias)에 의해
‘벽돌과 모타르 모델(Brick and Mortar)’로 명명되어졌으며,
모타르에 해당되는 세포간 지질은
세라마이드, 콜레스테롤 및 유리지방산으로
구성되어 있다.
8. 기타
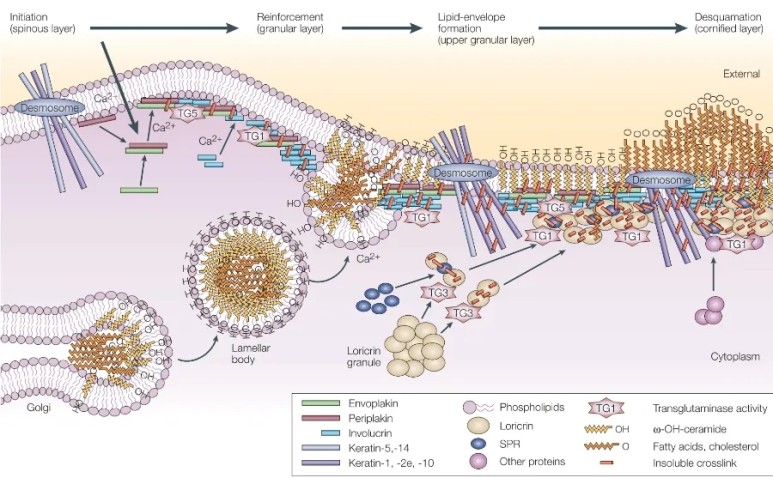
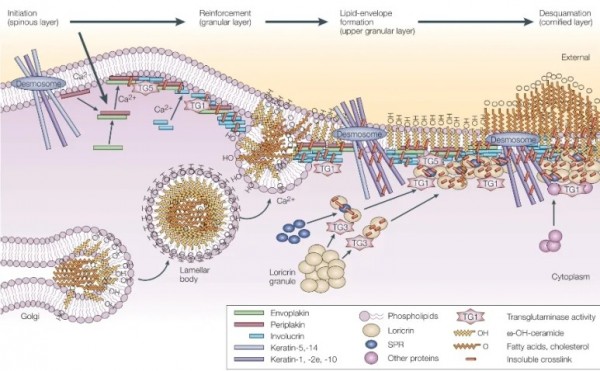
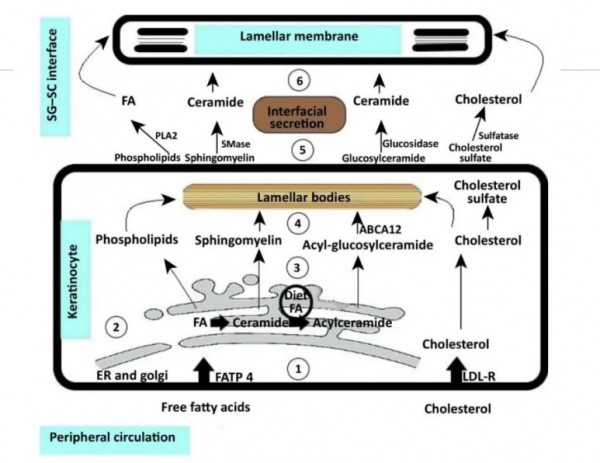
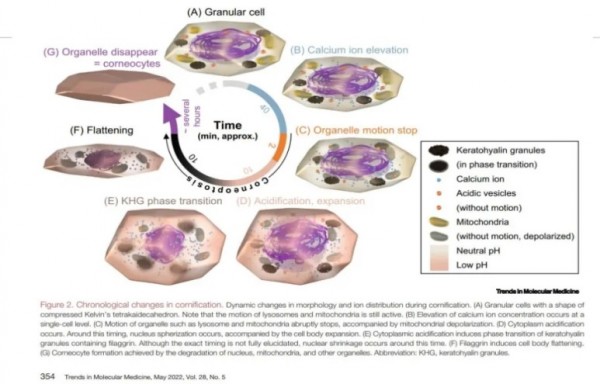
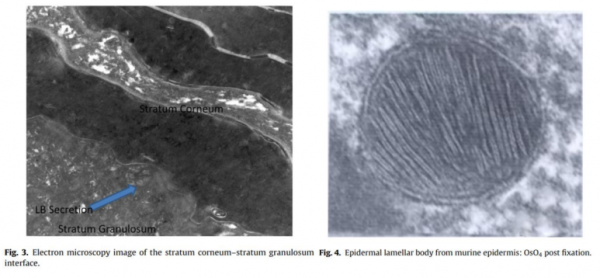
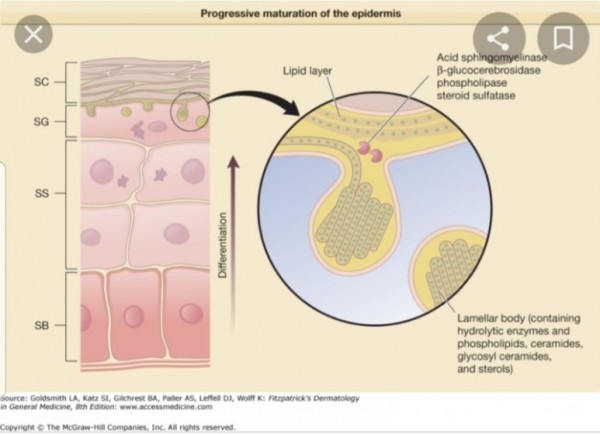
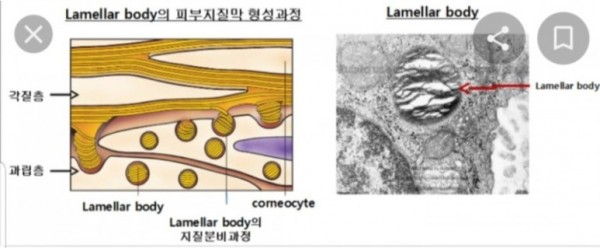
※ 각질층에서 세라마이드 형성
과립층 세포의 매끈소포체
(SER, smooth endoplasmic reticulum)에서 만들어져 골지체로 이동하여
라멜라바디를 형성하고
세포막과 퓨전되면서
각질세포간 지질로 배출됨.
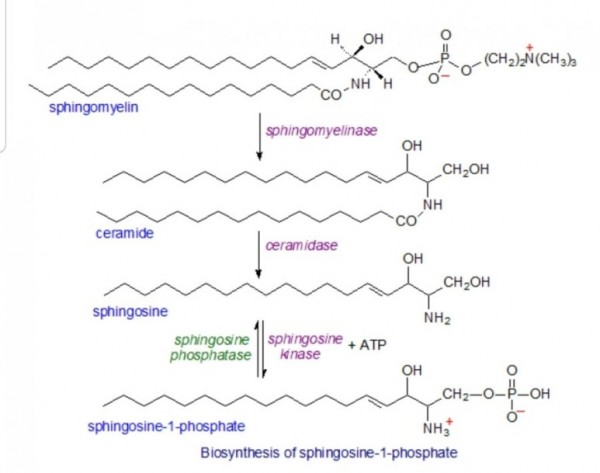
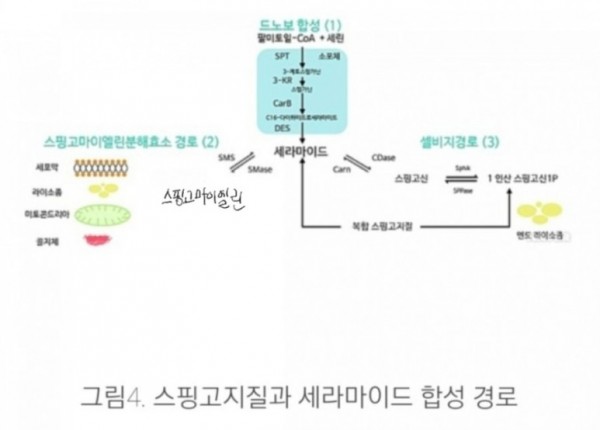
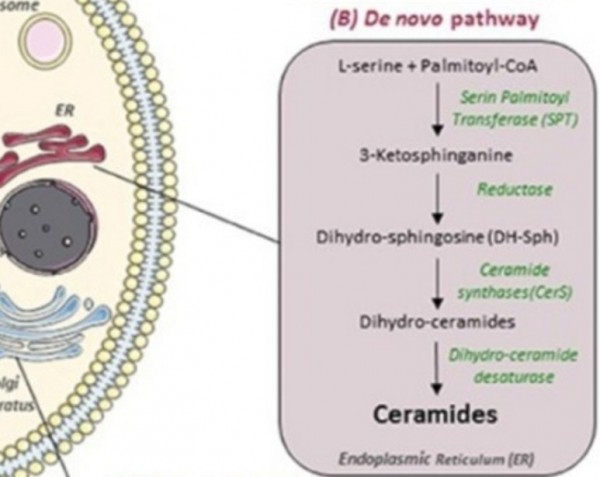
※ 합성경로
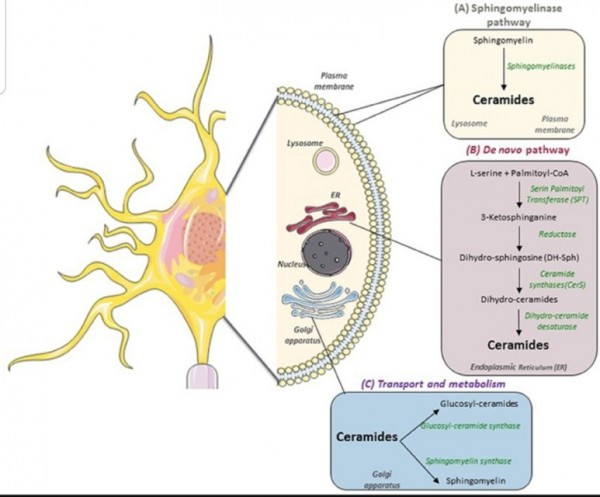
그림 1. 신경 세포의 스핑고지질 대사. 포유동물에서 스핑고지질을 생성하는 두 가지 주요 경로가 있습니다. (A) 리소좀과 원형질막에서 발생하고 스핑고미엘린(SM)이 스핑고미엘리나제(SM)에 의해 세라마이드로 분해되도록 하는 이화작용 스핑고미리나제 경로; (B) 3-케토스핑가닌을 형성하기 위해 팔미토일-CoA 및 L-세린의 축합과 함께 소포체(ER)의 세포질 면에서 시작하는 새로운 합성 경로 . (C) 그런 다음, 세라마이드가 골지체로 운반되어 글루코실-세라마이드 및 스핑고미엘린과 같은 보다 복잡한 스핑고리피드로 대사됩니다
There are three major pathways of ceramide generation.
First, the sphingomyelinase pathway uses an enzyme to break down sphingomyelin in the cell membrane
and release ceramide.
Second, the de novo pathway creates ceramide from less complex molecules.
Third, in the "salvage" pathway, sphingolipids that are broken down into sphingosine are reused by reacylation to form ceramide.
1) Sphingomyelin hydrolysis
Hydrolysis of sphingomyelin is catalyzed by the enzyme sphingomyelinase. Because sphingomyelin is one of the four common phospholipids found in the plasma membrane of cells, the implications of this method of generating ceramide is that the cellular membrane is the target of extracellular signals leading to programmed cell death. There has been research suggesting that when ionizing radiation causes apoptosis in some cells, the radiation leads to the activation of sphingomyelinase in the cell membrane and ultimately, to ceramide generation.[2]
2) De novo
De novo synthesis of ceramide begins with the condensation of palmitate and serine to form 3-keto-dihydrosphingosine. This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme serine palmitoyl transferase and is the rate-limiting step of the pathway. In turn, 3-keto-dihydrosphingosine is reduced to dihydrosphingosine, which is then followed by acylation by the enzyme (dihydro)ceramide synthase to produce dihydroceramide. The final reaction to produce ceramide is catalyzed by dihydroceramide desaturase. De novo synthesis of ceramide occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum. Ceramide is subsequently transported to the Golgi apparatus by either vesicular trafficking or the ceramide transfer protein CERT.
Once in the Golgi apparatus,
ceramide can be further metabolized
to other sphingolipids,
such as sphingomyelin and the complex glycosphingolipids.[3]
3) Salvage pathway
Constitutive degradation of sphingolipids and glycosphingolipids takes place in the acidic subcellular compartments, the late endosomes and the lysosomes, with the end goal of producing sphingosine. In the case of glycosphingolipids, exohydrolases acting at acidic pH optima cause the stepwise release of monosaccharide units from the end of the oligosaccharide chains, leaving just the sphingosine portion of the molecule, which may then contribute to the generation of ceramides. Ceramide can be further hydrolyzed by acid ceramidase to form sphingosine and a free fatty acid, both of which are able to leave the lysosome, unlike ceramide. The long-chain sphingoid bases released from the lysosome may then re-enter pathways for synthesis of ceramide and/or sphingosine-1-phosphate. The salvage pathway re-utilizes long-chain sphingoid bases to form ceramide through the action of ceramide synthase. Thus, ceramide synthase family members probably
trap free sphingosine released
from the lysosome
at the surface of the endoplasmic reticulum or in endoplasmic reticulum-associated membranes.
The salvage pathway has been estimated to contribute from 50% to 90% of sphingolipid biosynthesis.[4]
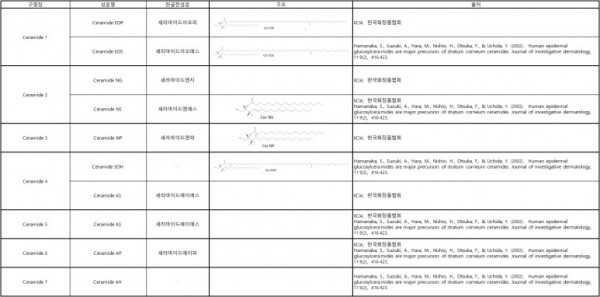
※ 세라마이드의 종류(과거)
세라마이드 1 Ceramide EOP
세라마이드 2 Ceramide NS
세라마이드 3 Ceramide NP
세라마이드 4, 5 Ceramide AS
세라마이드 6 Ceramide AP
※ 숫자로 명명은 사라짐
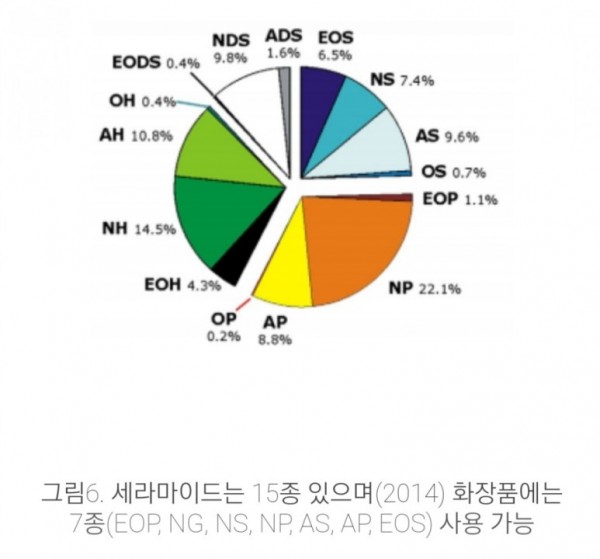
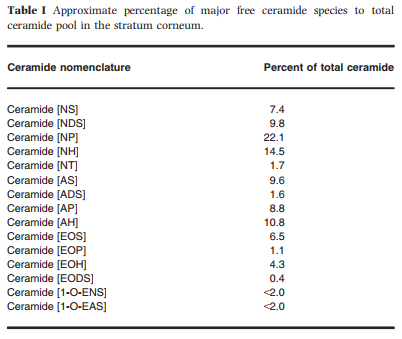
인간피부에서 발견되는 총 세라마이드 중 각 세라마이드 종류 분포도.
세라마이드엔피가(이하 세라마이드3)
22.1%로 가장 높은 수치로 발견 되는 것을 확인 할 수 있다.
※
우리 피부조직에 있는 세라마이드는
여러종류가 있습니다.
이 세라마이드들은 각 화학적 구조와 기능을 달리하지만,
우리 피부 속에서 다함께 작용합니다
(cooperative effect).
각 세라마이드 종류를 혼합하여
같이 사용하였을때에
시너지 효과가 있으며
CeramideNP(세라마이드 3)의
생체이용률(bioavailability)을
45% 이상으로
끌어올려주는 것으로 연구 된 바 있습니다.
※ 함께 사용하면 좋은 성분
세라마이드의 전구체 역할을 하는
스핑고신, 파이토스핑고신, 팔미틱애씨드,
글루코실세라마이드와 함께 사용하면 세라마이드 형성을 도와 피부 장벽 개선을 돕습니다.
세라마이드는 항산화 효과도 있어,
산화작용을 하는 레티놀과 함께 사용하면
산화 작용을 어느 정도 억제하여 줄 수 있어,
레티놀의 좋은 짝꿍입니다.
또한 항염작용도 우수하여 다소 자극적일 수 있는 레티놀의 염증작용을 억제하기 때문에
이 또한 세라마이드가 레티놀의 좋은 짝꿍 성분임을 시사하는 바입니다.
ㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡㅡ
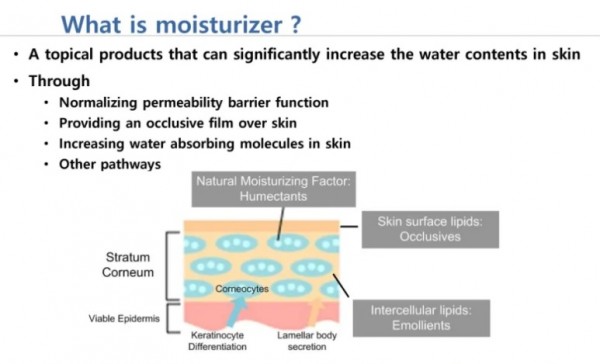
※ 세라마이드는
피부 각질 세포 간 지질성분의
대략 절반을 차지하는 왁스 제형의 지질로 우수한 보습제입니다.
장벽기능을 개선시킬 뿐만 아니라
밀폐제 역할도 한다.
유수분 밸런스를 잡아주며,
타이로시나제 발현을 억제하여
멜라닌의 생합성을 억제하기도 합니다.
항균과 항염에도 우수하여
여드름을 억제하기도 합니다.
또한 세라마이드는 항산화 기능도 있다.
http://www.biotimes.co.kr/news/articleView.html?idxno=3520(참조)
생체 활성 지질로서 세라마이드는
세포자멸사 , 세포 성장 정지, 분화,
세포 노화 , 세포 이동 및 부착을 비롯한 다양한 생리학적 기능을 합니다.[3]
암 , 신경변성 , 당뇨병 , 미생물 병인, 비만 및 염증을
포함한 여러 병리학적 상태에서 세라마이드와
그 하위 대사 산물의 역할이 제안되었습니다 . [5] [6]
세라마이드는 TLR4 수용체의
포화 지방 활성화의 결과로 합성될 때
골격근 인슐린 저항성을 유도 합니다. [7]
불포화 지방은 이러한 효과가 없습니다. [7]
세라마이드는 Akt/PKB 신호전달을 억제하여
많은 조직에서 인슐린 저항성을 유발 합니다. [8]
세라마이드에 의한 LDL 콜레스테롤의 응집은
동맥벽에 LDL 저류를 일으켜
죽상동맥경화증 을 유발 합니다. [9]
소포체 스트레스 유발로 당뇨 악화
미토콘드리아에서 세라마이드는
전자 수송 사슬을 억제하고
활성 산소 종의 생성을 유도 합니다. [11]
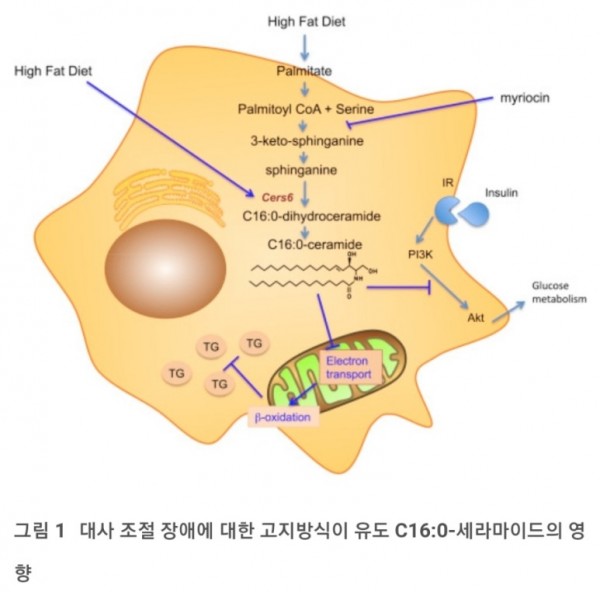
고지방 식단(HFD)을 섭취하는 야생형 마우스는 장쇄 세라마이드가 증가하고 포유류 C16:0-세라마이드 합성을 담당하는 효소인 CerS6의 발현이 선택적으로 증가한다는 것을 보여줍니다.
C16:0-Ceramide Signals Insulin Resistance
CELL METABOLISM VOLUME 20, ISSUE 5, P703-705, NOVEMBER 04, 2014
● 아폽토시스
세라마이드의 가장 많이 연구된 역할 중 하나는 세포자멸사 입니다.
Apoptosis(프로그램된 세포 사멸)는
정상적인 세포 항상성의 유지에 필수적이며
다양한 형태의 세포 스트레스에 대한
생리학적 반응입니다.
세라마이드 축적은 이온화 방사선, [2] [12]
UV 광선, [13] , TNF-알파 , [14] 및 화학요법제를
포함하는 다수의 세포사멸 약제로 세포를 처리한 후 발견되었습니다.
이것은 이러한 모든 약제의 생물학적 반응에서 세라마이드의 역할을 시사합니다.
암세포에서 세포자멸사를 유도하는 효과 때문에 세라마이드는 "종양 억제 지질"로 불립니다.
여러 연구에서 세포 사멸 사건에서
세라마이드의 특정 역할을 추가로 정의하려고 시도했으며 일부 증거는 세포자멸사를 유도하는 미토콘드리아 상류의 세라마이드 기능을 시사 합니다.
그러나 세포 사멸에서 세라마이드의 역할에 대한 연구의 상충되고 다양한 특성으로 인해
이 지질이 세포 사멸을 조절하는 메커니즘은
여전히 애매합니다. [15]
As a bioactive lipid, ceramide has been implicated in a variety of physiological functions including
apoptosis,
cell growth arrest,
differentiation,
cell senescence,
cell migration and adhesion.[3]
Roles for ceramide and its downstream metabolites have also been suggested in a number of pathological states including cancer, neurodegeneration,
diabetes, microbial pathogenesis,
obesity, and inflammation.[5][6]
Ceramides induce skeletal muscle
insulin resistance
when synthesized as a result of saturated fat activation of TLR4 receptors.[7]
Unsaturated fat does not have this effect.[7]
Ceramides induce insulin resistance
in many tissues by inhibition of Akt/PKB signaling.[8]
Aggregation of LDL cholesterol
by ceramide causes LDL retention in arterial walls, leading
to atherosclerosis.[9]
Ceramides cause endothelial dysfunction by activating protein phosphatase 2 (PP2A).[10]
In mitochondria, ceramide suppresses the electron transport chain and induces production of reactive oxygen species.[11]
1) Apoptosis
One of the most studied roles of ceramide pertains to its function as a proapoptotic molecule.
Apoptosis, or Type I programmed cell death, is essential for the maintenance of normal cellular homeostasis
and is an important physiological response to many forms of cellular stress.
Ceramide accumulation has been found following treatment of cells with a number of apoptotic agents including ionizing radiation,[2][12]
UV light,[13] TNFalpha,[14]
and chemotherapeutic agents.
This suggests a role for ceramide
in the biological responses of all these agents. Because of its apoptosis-inducing effects in cancer cells, ceramide has been termed the
"tumor suppressor lipid".
Several studies have attempted to define further the specific role of ceramide
in the events of cell death and some evidence suggests ceramide functions upstream of the mitochondria
in inducing apoptosis.
However, owing to the conflicting and variable nature of studies into the role of ceramide in apoptosis, the mechanism by which this lipid regulates apoptosis remains elusive.[15]
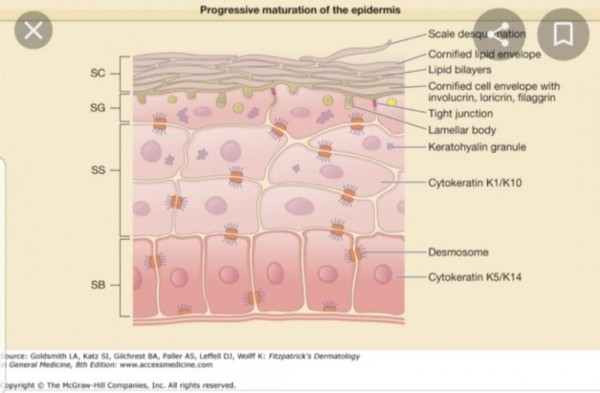
2) Skin
Ceramide is the main component of the stratum corneum of the epidermis layer of human skin.[16][17]
Together with cholesterol and saturated fatty acids, ceramide creates a water-impermeable, protective organ to prevent excessive water loss due to evaporation as well as a barrier against the entry of microorganisms.[17]
In the hyperplastic disorder psoriasis
the water permeability barrier is compromised.[18]
Ceramide VI is the most abundant ceramide of the skin, along with ceramide II, and has been exploited to model the organization of the stratum corneum lipidic network.[19][20]
The stratum corneum is composed of 50% ceramides, 25% cholesterol, and 15% free fatty acids.[18]
Key components of the extracellular lipid lamellae of the stratum corneum are
ultra long chain
(C28-C36)ceramides.[21]
※ 지방산 탄소수
단쇄지방산 4개
중쇄지방산 6개-10개
장쇄지방산 12-20개
초장쇄지방산 22-36개
With aging there is a decline in
ceramide and cholesterol in the stratum corneum of humans.[22]
A clinical trial using ceramide-rich wheat extract showed increased skin hydration in those taking the extract rather than the placebo.[23]
3) Hormonal
Inhibition of ceramide synthesis with myriocin in obese mice
may lead to both improved leptin signaling
and decreased insulin resistance
by decreasing SOCS-3 expression.[24]
An elevated level of ceramide
can cause insulin resistance by inhibiting the ability of insulin to activate the insulin signal
transduction pathway and/or via the activation of JNK.[25]
(참조) https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ceramide
#닥터오라클 #오라클코스메틱 #오라클피부과 #droracle #oracle_cosmetic #성분연구 #세라마이드 #Ceramide
#스핑고신
#spingosin
#세라마이드3
#세라마이드NP
#세라마이드EOP
#세라마이드NS
#스핑고마이엘린
#아실세라마이드
#Acylceramide
#울트라롱체인지방산
#롱체인지방산
#EOP
#NP
관련링크
댓글목록 0
등록된 댓글이 없습니다.